Denitrification Bed: Wastewater Treatment Explained
In the realm of wastewater treatment, denitrification beds play a crucial role in the process of removing harmful substances from wastewater. This article delves into the intricate details of denitrification beds, their function, design, operation, and significance in the larger context of wastewater treatment.
Wastewater treatment is a complex and multi-faceted process, and denitrification beds are one of the many components that contribute to its successful operation. Understanding the role and functionality of these beds is essential for anyone involved in the field of wastewater treatment, whether as a professional, a student, or a concerned citizen.
Understanding Denitrification
Before delving into the specifics of denitrification beds, it's important to first understand the process of denitrification itself. Denitrification is a microbial process that converts nitrate, a common pollutant in wastewater, into nitrogen gas which is then released into the atmosphere.
This process is an essential part of the nitrogen cycle, a series of chemical reactions that circulate nitrogen through the biosphere. Nitrogen, while essential for life, can be harmful in excessive amounts, particularly in the form of nitrate. Thus, denitrification serves as a natural method of nitrate removal, mitigating its potential harm.
Microorganisms and Denitrification
Denitrification is facilitated by a variety of microorganisms, primarily bacteria. These denitrifying bacteria are capable of using nitrate as an alternative to oxygen for respiration. In the absence of oxygen, these bacteria convert nitrate into nitrogen gas, a process known as anaerobic respiration.
These microorganisms are ubiquitous in nature and can be found in a variety of environments, including soils, sediments, and bodies of water. Their ability to thrive in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions makes them particularly effective at facilitating denitrification.
Significance of Denitrification in Wastewater Treatment
Denitrification is a critical process in wastewater treatment. Excessive nitrate in wastewater can lead to a variety of environmental issues, including eutrophication, a condition where excessive nutrients in bodies of water lead to dense plant growth and subsequent death, leading to a depletion of oxygen and harm to other aquatic life.
By converting nitrate into nitrogen gas, denitrification effectively removes this pollutant from wastewater, preventing its release into the environment. This process is a key component of the biological nutrient removal (BNR) process in wastewater treatment.
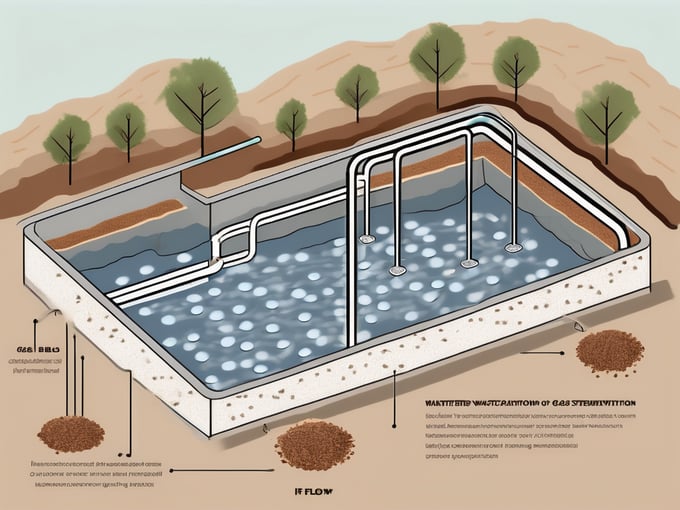
Denitrification Beds: Design and Function
Now that we've established an understanding of denitrification, we can delve into the specifics of denitrification beds. These are engineered systems designed to facilitate the denitrification process. They are typically constructed as large, shallow beds filled with a carbon source, such as wood chips, which serve as a food source for the denitrifying bacteria.
The design of these beds is crucial to their function. They must be designed to create an environment conducive to the growth and activity of denitrifying bacteria. This typically involves creating conditions of low oxygen and high nitrate, which encourage the bacteria to utilize nitrate for respiration.
Key Components of Denitrification Beds
The primary components of a denitrification bed include the bed itself, the carbon source, the wastewater feed system, and the effluent collection system. The bed is typically constructed of a durable material such as concrete or plastic, and is filled with a carbon source such as wood chips.
The wastewater feed system delivers the nitrate-rich wastewater to the bed, while the effluent collection system collects the treated wastewater for discharge or further treatment. The design and operation of these components are critical to the effective function of the denitrification bed.
Role of Carbon Source
The carbon source in a denitrification bed serves as a food source for the denitrifying bacteria. As these bacteria consume the carbon, they also convert nitrate into nitrogen gas. The choice of carbon source is critical, as it must be readily available, cost-effective, and capable of supporting the growth and activity of the bacteria.
Wood chips are a commonly used carbon source due to their availability and effectiveness. They provide a slow, steady release of carbon, which supports the sustained activity of the bacteria. Other potential carbon sources include straw, sawdust, and other organic materials.
Operation and Maintenance of Denitrification Beds
Effective operation and maintenance of denitrification beds are essential to their performance. This involves regular monitoring of nitrate levels in the influent and effluent, as well as the condition of the bed and its components.
Over time, the carbon source in the bed will be consumed by the bacteria and will need to be replenished. This typically involves the addition of fresh carbon material to the bed. The frequency of this replenishment will depend on the specific design and operation of the bed.
Monitoring and Control
Regular monitoring of the denitrification bed is crucial to ensure its effective operation. This typically involves sampling the influent and effluent to measure nitrate levels, as well as monitoring the physical condition of the bed and its components.
Control measures may include adjustments to the wastewater feed rate, the addition of fresh carbon material, or other interventions as needed. The goal is to maintain optimal conditions for denitrification, ensuring the effective removal of nitrate from the wastewater.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance of the denitrification bed is essential to its longevity and performance. This may involve the replacement of worn or damaged components, the addition of fresh carbon material, or other interventions as needed.
Troubleshooting may be required if the bed is not performing as expected. This may involve investigating potential issues such as inadequate nitrate removal, clogging of the bed, or other operational problems. The resolution of these issues may require adjustments to the operation of the bed, repairs or replacements of components, or other interventions.
Advantages and Limitations of Denitrification Beds
Denitrification beds offer a number of advantages in the treatment of wastewater. They are a cost-effective method of nitrate removal, as they utilize a natural process and require relatively low operational and maintenance costs. They are also versatile and can be designed to treat a wide range of nitrate concentrations.
However, denitrification beds also have their limitations. They require a significant amount of space, which may not be available in all settings. They also require a steady supply of a suitable carbon source, which may not be readily available in all regions. Furthermore, their performance can be influenced by a variety of factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of other substances in the wastewater.
Advantages of Denitrification Beds
One of the primary advantages of denitrification beds is their cost-effectiveness. They utilize a natural process to remove nitrate from wastewater, requiring minimal energy input. The use of a carbon source such as wood chips also provides a slow, steady release of carbon, supporting the sustained activity of the denitrifying bacteria.
Denitrification beds are also versatile and can be designed to treat a wide range of nitrate concentrations. This makes them suitable for a variety of applications, from small-scale residential systems to large-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants.
Limitations of Denitrification Beds
Despite their advantages, denitrification beds also have their limitations. One of the primary limitations is their space requirement. Denitrification beds are typically large, shallow systems, requiring a significant amount of space. This may not be available in all settings, particularly in urban areas.
Another limitation is the requirement for a suitable carbon source. While wood chips are a commonly used carbon source, they may not be readily available in all regions. Furthermore, the performance of denitrification beds can be influenced by a variety of factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of other substances in the wastewater. These factors must be carefully managed to ensure the effective operation of the bed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, denitrification beds play a crucial role in the treatment of wastewater, facilitating the removal of harmful nitrate pollutants. Understanding their design, operation, and maintenance is essential for anyone involved in the field of wastewater treatment.
While they have their limitations, denitrification beds offer a cost-effective and versatile method of nitrate removal. With careful design, operation, and maintenance, they can be an effective component of a comprehensive wastewater treatment system.



