
Dissolved Air Flotation: Wastewater Treatment Explained
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a widely used wastewater treatment process that separates solids, oils, and greases from wastewater, thereby improving its overall quality. This process is particularly effective in treating industrial wastewater, where it plays a crucial role in preventing harmful substances from entering the environment. The DAF process is complex and involves several steps, each of which contributes to its effectiveness.
Understanding the intricacies of the DAF process requires a deep dive into its various components and the science behind them. This glossary article aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of the DAF process, its components, and its role in wastewater treatment. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of DAF and its importance in maintaining environmental health.
Overview of Dissolved Air Flotation
Dissolved Air Flotation is a water treatment process where air is dissolved into the water under pressure and then released at atmospheric pressure in a flotation tank. The released air forms tiny bubbles that adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device.
DAF is a preferred method for treating wastewater due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It is particularly effective in treating wastewater with high levels of fats, oils, and greases, as well as industrial wastewater containing heavy metals and other pollutants. The process is also highly adaptable, allowing it to be used in a variety of wastewater treatment scenarios.
History of DAF
The concept of Dissolved Air Flotation has been around for over a century, with the first DAF systems being used in the early 1900s. These early systems were primarily used in the pulp and paper industry to remove fibers and other solids from water. Over time, the technology evolved and began to be used in a wider range of industries, including food processing, oil and gas, and more.
Today, DAF systems are a common sight in wastewater treatment plants around the world. They are recognized for their ability to effectively remove a wide range of pollutants from wastewater, making them a key component of modern wastewater treatment strategies.
Components of a DAF System
A typical DAF system consists of several key components, each of which plays a crucial role in the overall process. These components include the pressure tank, air compressor, diffuser, flotation tank, and skimmer. Understanding the function of each of these components is essential to understanding how DAF works.
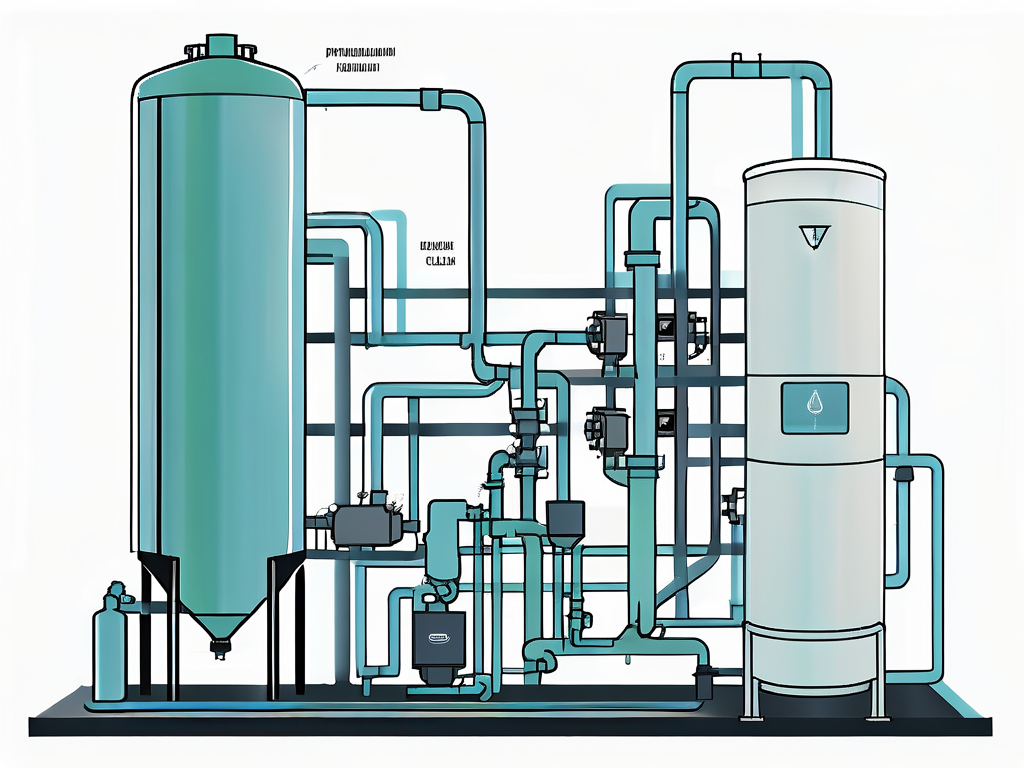
The pressure tank is where the air is dissolved into the water. This is achieved by pumping air into the tank under high pressure, which causes the air to dissolve. The air compressor provides the air that is pumped into the pressure tank, while the diffuser ensures that the air is evenly distributed throughout the tank.
Flotation Tank and Skimmer
The flotation tank is where the actual flotation process takes place. The pressurized water from the pressure tank is released into the flotation tank at atmospheric pressure. This causes the dissolved air to form tiny bubbles, which attach to the suspended matter and cause it to float to the surface.
The skimmer is used to remove the floating matter from the surface of the water. This is typically done using a mechanical device that skims the surface of the water and collects the floating matter. The collected matter is then removed from the system and disposed of appropriately.
DAF Process
The DAF process begins with the pressurization of water in the pressure tank. Air is pumped into the tank under high pressure, causing it to dissolve into the water. This pressurized water is then released into the flotation tank at atmospheric pressure.
As the pressurized water is released, the dissolved air forms tiny bubbles. These bubbles attach to the suspended matter in the water, causing it to float to the surface. The floating matter is then removed by the skimmer, resulting in cleaner water.
Coagulation and Flocculation
Before the DAF process can begin, the wastewater must first undergo coagulation and flocculation. These are pre-treatment steps that prepare the wastewater for the DAF process. Coagulation involves adding a coagulant to the wastewater, which causes the suspended particles to clump together.
Flocculation is the process of gently mixing the coagulated water to encourage the formation of larger flocs. These larger flocs are easier for the DAF system to remove, making coagulation and flocculation important steps in the overall process.
Applications of DAF
DAF is used in a wide range of industries to treat wastewater. Some of the most common applications include food and beverage processing, oil and gas production, and pulp and paper manufacturing. In these industries, DAF is used to remove fats, oils, greases, and other pollutants from wastewater.
DAF is also used in municipal wastewater treatment plants to remove suspended solids and other contaminants. In these applications, DAF is often used in conjunction with other treatment processes to ensure the highest level of water quality.
Industrial Wastewater Treatment
In industrial settings, DAF is often used as a pre-treatment step before the wastewater is further treated using other methods. This is because DAF is particularly effective at removing large amounts of solids, oils, and greases, which are common in industrial wastewater.
By removing these substances early in the treatment process, DAF helps to reduce the load on downstream treatment processes. This can result in significant cost savings and improved overall treatment efficiency.
Advantages and Limitations of DAF
DAF offers several advantages over other wastewater treatment methods. These include high removal efficiency, adaptability to a wide range of wastewater types, and the ability to handle high loads of pollutants. Additionally, DAF systems are relatively compact, making them suitable for use in areas with limited space.
However, DAF also has some limitations. These include the need for careful control of the process conditions to ensure optimal performance, the potential for the formation of harmful by-products, and the need for regular maintenance to prevent system failures.
Environmental Impact
Despite its limitations, DAF plays a crucial role in protecting the environment. By removing harmful pollutants from wastewater, DAF helps to prevent these substances from entering the environment. This not only protects the health of aquatic ecosystems but also helps to ensure the safety of our water supplies.
However, it's important to note that the sludge produced by DAF systems must be properly disposed of to prevent environmental contamination. This often involves further treatment to reduce the volume of the sludge and make it safe for disposal.
Future of DAF
As our understanding of wastewater treatment continues to evolve, so too does the technology used in the process. DAF is no exception, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the process.
Future advancements in DAF technology may include the development of more efficient air dissolving systems, improved skimming devices, and more effective treatment chemicals. These advancements have the potential to make DAF an even more valuable tool in our ongoing efforts to protect the environment and ensure the availability of clean water.



