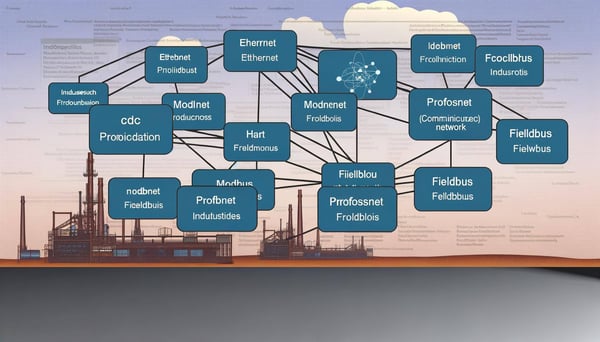
Fundamentals of CC-Link Industrial Networks
In the world of industrial automation, communication protocols play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless interaction between different devices and systems. Among the myriad of protocols available, CC-Link Industrial Networks have emerged as a robust and reliable solution for industrial communication. This article delves into the fundamentals of CC-Link Industrial Networks, exploring its architecture, benefits, and applications.
Understanding CC-Link Industrial Networks
The CC-Link Industrial Network is a high-speed, high-performance open industrial network technology that enables devices from numerous manufacturers to communicate. It was developed by Mitsubishi Electric and has gained widespread acceptance in Asia, particularly in Japan, and is gradually gaining traction worldwide.
CC-Link stands for Control and Communication Link, reflecting its dual function of controlling devices and facilitating communication between them. It supports both cyclic and transient communication, making it versatile for a variety of industrial applications.
Architecture of CC-Link Industrial Networks
The architecture of CC-Link Industrial Networks is based on the master-slave model. The master, also known as the network master station, controls the communication on the network. It initiates data exchange with the slave devices, also referred to as the network slave stations.
One of the unique features of CC-Link is that it allows for both point-to-point and shared memory communication. In point-to-point communication, the master station communicates directly with each slave station. In shared memory communication, all devices share a common memory area, enabling efficient data exchange.
Types of CC-Link Networks
There are three types of CC-Link networks: CC-Link, CC-Link IE Control, and CC-Link IE Field. Each type is designed for specific applications and offers different features.
CC-Link is the standard network for general industrial automation. CC-Link IE Control is an Ethernet-based network designed for control applications, while CC-Link IE Field is an Ethernet-based network designed for field devices.
Benefits of CC-Link Industrial Networks
CC-Link Industrial Networks offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice for industrial automation. These benefits include high-speed communication, flexibility, and ease of integration.
CC-Link networks can achieve communication speeds of up to 10 Mbps, which is significantly faster than many other industrial networks. This high-speed communication enables real-time control and monitoring of devices, which is crucial in many industrial applications.
Flexibility and Scalability
CC-Link Industrial Networks are highly flexible and scalable. They can support a large number of devices - up to 64 devices on a single network for CC-Link and up to 120 devices for CC-Link IE. This makes them suitable for both small and large-scale industrial applications.
Furthermore, CC-Link networks can be easily expanded by adding more devices to the network. This scalability makes it easy to adapt the network to changing requirements, without the need for significant modifications or upgrades.
Integration with Other Systems
Another major advantage of CC-Link Industrial Networks is their ease of integration with other systems. CC-Link networks can be seamlessly integrated with other industrial networks and protocols, such as Profibus, DeviceNet, and Modbus. This interoperability makes CC-Link a versatile solution for multi-vendor environments.
Moreover, CC-Link networks support a wide range of devices, from sensors and actuators to PLCs and HMIs. This means that you can use CC-Link to connect virtually any device in your industrial automation system.
Applications of CC-Link Industrial Networks
Thanks to their high-speed communication, flexibility, and ease of integration, CC-Link Industrial Networks are used in a wide range of applications. These include manufacturing, process control, and building automation, among others.

In manufacturing, CC-Link networks are used to connect machines and devices on the factory floor, enabling real-time monitoring and control. This helps to improve productivity and efficiency, reduce downtime, and ensure product quality.
Process Control
In process control, CC-Link networks are used to connect sensors, actuators, and controllers. This enables precise control of processes, such as temperature, pressure, and flow, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Furthermore, the high-speed communication of CC-Link networks enables real-time data acquisition, which is crucial for process monitoring and optimization.
Building Automation
In building automation, CC-Link networks are used to connect various building systems, such as HVAC, lighting, and security systems. This enables centralized control and monitoring, improving energy efficiency and building comfort.
Moreover, the flexibility and scalability of CC-Link networks make them suitable for both small and large buildings, from residential homes to commercial complexes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CC-Link Industrial Networks offer a robust, flexible, and high-speed solution for industrial communication. Whether you're looking to improve your manufacturing processes, optimize your process control, or enhance your building automation, CC-Link has the capabilities to meet your needs.
With its high-speed communication, flexibility, ease of integration, and wide range of applications, CC-Link is set to play a key role in the future of industrial automation.