Fundamentals of FINS
In the world of industrial automation, communication protocols play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless interaction between devices. One such protocol that has gained significant traction is the Factory Interface Network Service, commonly known as FINS. This article delves into the intricacies of FINS, its importance in industrial automation, and how it facilitates efficient communication between devices.
Understanding FINS
Developed by Omron, FINS is a proprietary communication protocol that enables data exchange between Omron PLCs and other devices. It is a part of the Sysmac family, a comprehensive system that integrates automation and control. FINS was designed to be flexible, robust, and easy to implement, making it a preferred choice for many industrial applications.

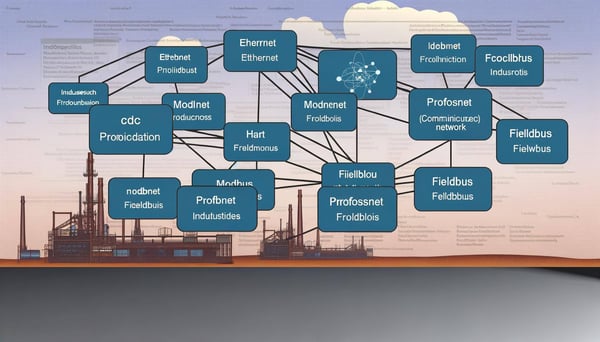
One of the key features of FINS is its ability to support different physical layers including Ethernet, Serial, and Controller Link networks. This versatility allows it to be used in a wide range of industrial settings, from small-scale applications to large, complex systems. Furthermore, FINS is not limited to Omron devices alone. With the right configuration, it can communicate with devices from other manufacturers, enhancing its usability.
Working Principle of FINS
FINS operates based on the Client-Server model. The client, often a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a Human Machine Interface (HMI), sends a command to the server, which could be another PLC or a network device. The server then processes the command and sends back a response.
The communication in FINS is facilitated through FINS frames, which carry the command and response data. Each frame consists of a header and a data field. The header includes information such as the command code, the source and destination addresses, while the data field contains the actual command or response data.
Benefits of Using FINS
FINS offers numerous benefits that make it a valuable asset in industrial automation. Its ability to support multiple physical layers makes it adaptable to various industrial environments. Whether it's a small manufacturing unit or a large-scale industrial plant, FINS can be effectively implemented to ensure smooth communication between devices.
Another significant advantage of FINS is its ease of configuration. Unlike some other industrial protocols that require complex setup processes, FINS can be easily configured using standard tools. This not only simplifies the implementation process but also reduces the time and effort required to get the system up and running.
Implementing FINS in Your System
Implementing FINS in your system involves a few key steps. The first step is to determine the physical layer that you will be using. As mentioned earlier, FINS supports Ethernet, Serial, and Controller Link networks, so you can choose the one that best suits your requirements.
Once you've decided on the physical layer, the next step is to configure the FINS parameters. This includes setting the source and destination addresses, the command code, and the data field. The configuration process can be easily carried out using standard tools provided by Omron.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FINS is a versatile and robust communication protocol that can significantly enhance the efficiency of industrial automation systems. Its flexibility, ease of configuration, and support for multiple physical layers make it a valuable tool for any industrial application. Whether you're looking to improve the communication between your devices or streamline your automation processes, FINS could be the solution you need.
As industrial automation continues to evolve, protocols like FINS will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of the industry. By understanding and implementing these protocols, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and ensure their systems are ready for the challenges of tomorrow.