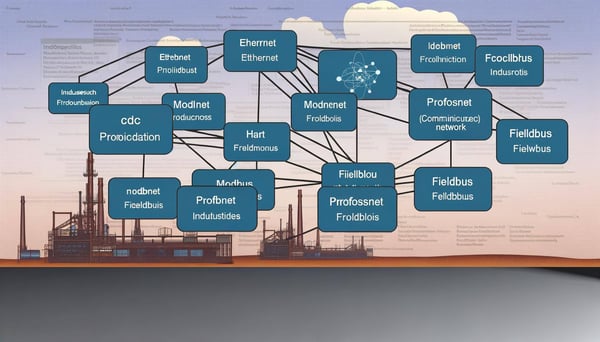
Fundamentals of GPRS
In the world of industrial communication, protocols play a crucial role in ensuring seamless and efficient data transmission. Among the myriad of protocols available, General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) stands out as a reliable and robust solution. This article delves into the fundamentals of GPRS, exploring its features, benefits, and applications in the industrial sector.
Understanding GPRS
General Packet Radio Service, commonly known as GPRS, is a packet-oriented mobile data standard on the 2G and 3G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). Introduced in the late 90s, GPRS was a revolutionary step towards modern mobile communications, providing moderate-speed data transfer by using unused time division multiple access (TDMA) channels in, for example, the GSM system.
Unlike traditional circuit-switched data on mobile systems, GPRS involves packet-switched data. This means data is broken down into packets and transmitted over an IP network. The primary advantage of this approach is the efficient use of available bandwidth, making GPRS a cost-effective solution for mobile data transmission.
Key Features of GPRS
GPRS comes packed with a host of features that make it a preferred choice for many industries. Let's explore these in detail.
High-Speed Data Transmission
One of the most significant features of GPRS is its high-speed data transmission. GPRS offers data rates of 56-114 kbps, making it faster than traditional dial-up connections. This speed is sufficient for most industrial applications that require real-time data transmission.
Moreover, GPRS supports a wide range of data services, including WAP access, SMS, MMS, and Internet communication services such as email and web browsing. These services open up a plethora of opportunities for industries to leverage GPRS for their communication needs.
Always-On Connectivity
Another notable feature of GPRS is its 'always-on' connectivity. Unlike dial-up connections, which require a user to establish a connection each time they want to transmit data, GPRS is always connected as long as the device is within the coverage area of the network. This feature is particularly beneficial for industries that require constant monitoring and control of their operations.
Furthermore, the 'always-on' connectivity of GPRS means that users are only charged for the amount of data they transmit, not the duration of their connection. This billing method makes GPRS a cost-effective solution for industries that need continuous data transmission.
Applications of GPRS in the Industrial Sector
GPRS has found widespread applications in various industrial sectors due to its robust features and benefits. Here are a few examples:
Remote Monitoring and Control
Industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and utilities often have remote sites that require constant monitoring and control. GPRS provides a reliable and cost-effective solution for these requirements. With its high-speed data transmission and 'always-on' connectivity, GPRS enables real-time monitoring and control of these sites, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
Moreover, GPRS supports a wide range of industrial protocols, making it compatible with various industrial devices and systems. This compatibility further enhances its applicability in the industrial sector.
Asset Tracking
Asset tracking is another area where GPRS shines. Industries such as logistics and transportation use GPRS to track their assets in real-time. This tracking helps in improving asset utilization, reducing theft, and ensuring timely delivery of goods.
Furthermore, with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), GPRS is playing a crucial role in enabling IoT applications in the industrial sector. These applications range from predictive maintenance and process automation to smart metering and energy management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GPRS is a robust and reliable industrial protocol that offers numerous benefits, including high-speed data transmission, 'always-on' connectivity, and compatibility with various industrial protocols. Its applications in remote monitoring and control, asset tracking, and IoT make it a preferred choice for many industries.
As we move towards a more connected and automated industrial landscape, the role of GPRS is set to become even more critical. Therefore, understanding the fundamentals of GPRS is essential for anyone involved in the industrial sector.