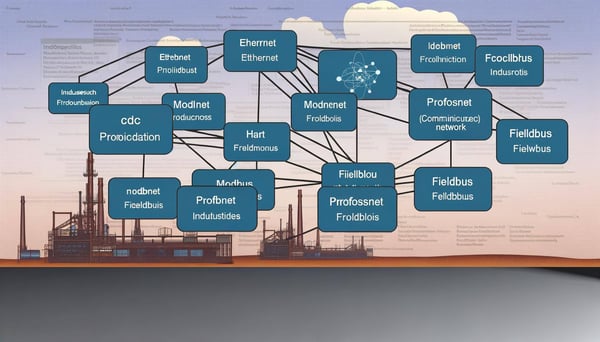
Fundamentals of Modbus PEMEX
In the world of industrial automation, communication protocols play a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of systems. One such protocol that has gained significant attention is Modbus PEMEX, a variant of the standard Modbus protocol. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the Modbus PEMEX protocol, its fundamentals, and its applications in the industrial sector.
Understanding Modbus Protocol
Before delving into the specifics of Modbus PEMEX, it is crucial to understand the basics of the Modbus protocol. Modbus is a communication protocol developed in 1979 for use with programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Over the years, it has become a de facto standard communication protocol, and it is now a common choice for connecting industrial electronic devices.
The Modbus protocol is based on a master/slave architecture where the master device initiates the communication. The slaves, or servers, respond by supplying the requested data to the master, or by performing the action requested in the query. Modbus operates using a simple command structure, making it easy to deploy and maintain.
Introduction to Modbus PEMEX
Modbus PEMEX is a variant of the standard Modbus protocol. It was developed by the Mexican state oil company, PEMEX, to meet their specific needs. The primary difference between Modbus PEMEX and the standard Modbus protocol lies in the data format and the use of function codes.
Modbus PEMEX uses a unique data format that includes additional fields for error checking and device identification. This makes it more robust and reliable, particularly in harsh industrial environments where communication errors can have serious consequences. Moreover, Modbus PEMEX uses specific function codes that are not found in the standard Modbus protocol, allowing for more complex and specific commands to be sent.
Key Features of Modbus PEMEX
Robust Error Checking
One of the key features of Modbus PEMEX is its robust error checking mechanism. This is achieved through the use of a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) field in the data format. The CRC is a powerful error-detection tool that helps to ensure the integrity of the data being transmitted.
By including a CRC field in every data packet, Modbus PEMEX can quickly identify and correct any errors that occur during transmission. This makes it an ideal choice for industrial applications where reliable communication is critical.
Device Identification
Another significant feature of Modbus PEMEX is its device identification mechanism. Each device in a Modbus PEMEX network is assigned a unique identifier, which is included in every communication packet. This allows the master device to easily identify and communicate with specific devices on the network.
Device identification is particularly useful in large industrial networks where there may be hundreds or even thousands of devices. It simplifies network management and improves the efficiency of communication.
Applications of Modbus PEMEX
Due to its robustness and reliability, Modbus PEMEX is widely used in a variety of industrial applications. Its primary use is in the oil and gas industry, where it was initially developed. Here, it is used to monitor and control equipment such as pumps, valves, and sensors.
However, the use of Modbus PEMEX is not limited to the oil and gas industry. It is also used in other industries such as manufacturing, power generation, and water treatment. In these industries, Modbus PEMEX is used to control and monitor a wide range of equipment, from conveyor belts to generators to water treatment plants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Modbus PEMEX is a powerful and versatile communication protocol that is well-suited to the demands of the industrial sector. Its robust error checking and device identification mechanisms make it a reliable choice for a wide range of applications.
Whether you are involved in the oil and gas industry, manufacturing, power generation, or water treatment, Modbus PEMEX can provide a robust and reliable communication solution for your industrial automation needs.