
Jar Test: Wastewater Treatment Explained
The Jar Test is a common laboratory procedure used to simulate the coagulation/flocculation process in a wastewater treatment plant. It is an essential tool for determining the appropriate chemical dosages required for effective treatment, and for optimizing the performance of the treatment process.
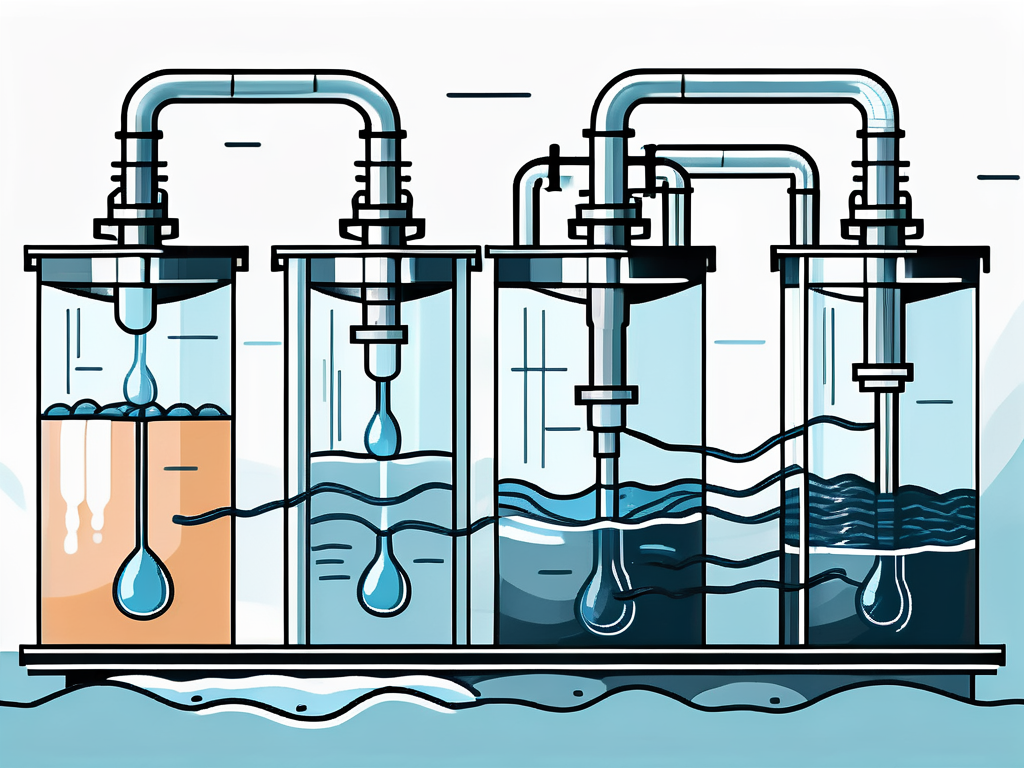
This method involves the use of a multi-station gang stirrer that holds a series of six or more jars, where each jar represents a different test condition. The process allows for the simultaneous comparison of different treatment options, providing valuable insights into the most effective treatment method.
Understanding the Jar Test
The Jar Test is a critical part of the wastewater treatment process. It is used to determine the optimal dose of coagulant and flocculant chemicals needed to remove suspended and colloidal particles from the wastewater. These particles, which can include organic and inorganic materials, bacteria, viruses, and other pollutants, are often too small to be removed by physical filtration processes alone.
By adding coagulants and flocculants to the water, these small particles are made to aggregate into larger clumps, or flocs, which can then be more easily removed by sedimentation, flotation, or filtration. The Jar Test helps to identify the best type and amount of chemical to use for this process, ensuring the most efficient and effective treatment.
Components of the Jar Test
The Jar Test apparatus consists of a series of transparent jars, usually six, arranged in a row on a gang stirrer. Each jar is filled with a sample of the wastewater to be treated. The gang stirrer allows for the simultaneous stirring of all the jars at the same speed, ensuring consistent test conditions.
Each jar represents a different test condition, with varying amounts or types of coagulant and flocculant added. This allows for a direct comparison of the effectiveness of different treatment options. The results of the Jar Test are then used to determine the optimal treatment conditions for the full-scale wastewater treatment plant.
Procedure of the Jar Test
The Jar Test procedure involves several steps. First, a sample of the wastewater to be treated is added to each jar. Then, the coagulant is added, and the water is stirred rapidly to distribute the coagulant evenly throughout the water. This rapid mixing stage is followed by a slow mixing stage, which encourages the formation of flocs.
After the slow mixing stage, the stirring is stopped, and the flocs are allowed to settle to the bottom of the jar. The clarity of the water above the settled flocs is then observed and compared across the different jars. The jar with the clearest water indicates the most effective treatment condition.
Types of Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and flocculants are chemicals that promote the aggregation of small particles into larger flocs. Coagulants work by neutralizing the charge on the particles, allowing them to come together, while flocculants help to bind the particles together into larger clumps.
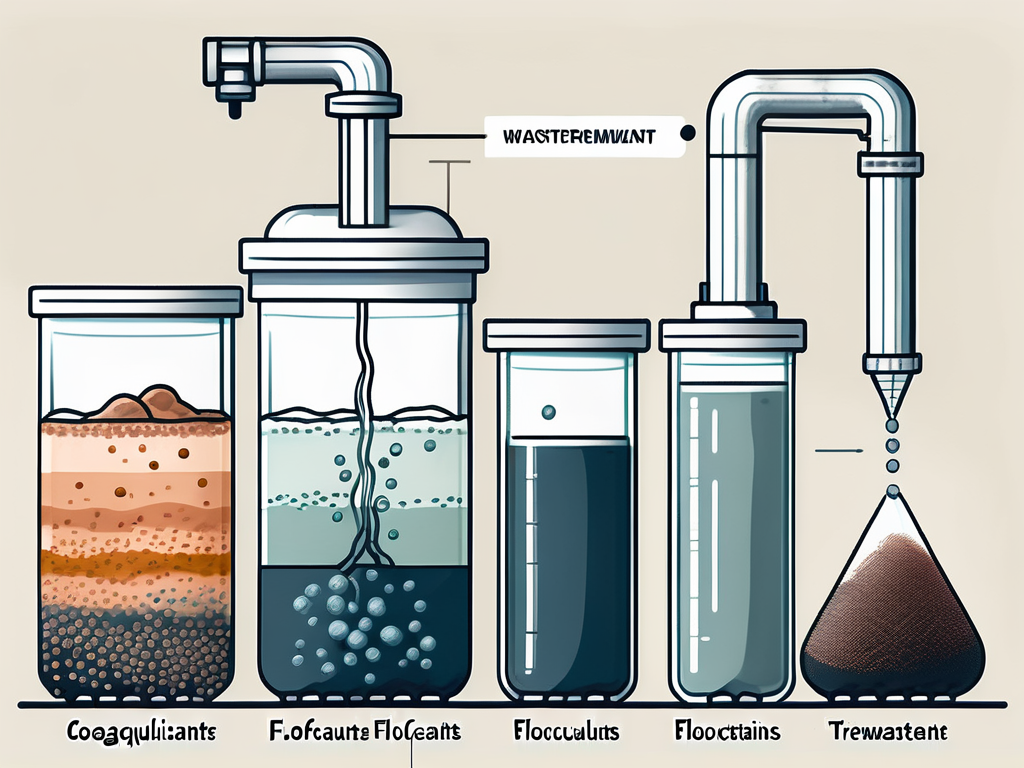
There are many different types of coagulants and flocculants, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of coagulant and flocculant depends on the specific characteristics of the wastewater, including the type and concentration of particles, the pH of the water, and other factors.
Common Coagulants
Common coagulants used in wastewater treatment include aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride. These chemicals work by neutralizing the charge on the particles in the water, allowing them to come together. The choice of coagulant depends on the specific characteristics of the wastewater, including the type and concentration of particles, the pH of the water, and other factors.
Alum is a widely used coagulant that is effective for a wide range of water conditions. However, it can cause a decrease in the pH of the water, which may require the addition of a pH adjusting chemical. Ferric chloride and polyaluminum chloride are also commonly used, and can be more effective than alum for certain types of wastewater.
Common Flocculants
Flocculants are chemicals that help to bind the coagulated particles together into larger clumps, or flocs. They are typically polymers, with a long chain structure that allows them to bind multiple particles together. There are many different types of flocculants, including natural polymers, synthetic polymers, and inorganic polymers.
Natural polymers, such as chitosan and alginate, are biodegradable and environmentally friendly, but may not be as effective as synthetic polymers for certain types of wastewater. Synthetic polymers, such as polyacrylamide, are highly effective, but can be more expensive and less environmentally friendly. Inorganic polymers, such as polyaluminum chloride, can be used as both a coagulant and a flocculant.
Interpreting Jar Test Results
The results of the Jar Test are used to determine the optimal treatment conditions for the full-scale wastewater treatment plant. The jar with the clearest water indicates the most effective treatment condition. However, it is also important to consider other factors, such as the amount of sludge produced, the pH of the treated water, and the cost of the chemicals.
It is also important to note that the Jar Test is a laboratory procedure, and the results may not always translate directly to the full-scale treatment plant. Other factors, such as the mixing and settling conditions in the plant, may affect the effectiveness of the treatment. Therefore, the results of the Jar Test should be used as a guide, and the treatment conditions should be adjusted as necessary based on the performance of the full-scale plant.
Factors Affecting Jar Test Results
There are many factors that can affect the results of the Jar Test. These include the characteristics of the wastewater, the type and amount of coagulant and flocculant used, the mixing and settling conditions, and the temperature of the water.
The characteristics of the wastewater, such as the type and concentration of particles, the pH of the water, and the presence of other chemicals, can greatly affect the effectiveness of the coagulant and flocculant. The type and amount of coagulant and flocculant used can also have a significant impact on the results. Too much or too little of these chemicals can lead to poor treatment performance.
Adjusting Treatment Based on Jar Test Results
The results of the Jar Test are used to adjust the treatment conditions in the full-scale wastewater treatment plant. If the Jar Test indicates that a certain type or amount of coagulant or flocculant is more effective, then this change can be implemented in the plant. However, it is important to monitor the performance of the plant closely after any changes are made, to ensure that the treatment is still effective.
It is also important to conduct the Jar Test regularly, as the characteristics of the wastewater can change over time. Regular testing allows for the treatment conditions to be adjusted as necessary, ensuring the most efficient and effective treatment at all times.
Limitations and Considerations of the Jar Test
While the Jar Test is a valuable tool for optimizing the wastewater treatment process, it is important to be aware of its limitations. The Jar Test is a laboratory procedure, and the conditions in the lab may not perfectly replicate the conditions in the full-scale treatment plant. Therefore, the results of the Jar Test should be used as a guide, and the treatment conditions should be adjusted as necessary based on the performance of the full-scale plant.
It is also important to consider the cost and environmental impact of the coagulant and flocculant chemicals. While these chemicals are necessary for effective treatment, they can be expensive and may have negative environmental impacts. Therefore, it is important to use these chemicals judiciously, and to explore other treatment options, such as biological treatment methods, where possible.
Scaling Up From Jar Test Results
Scaling up from the results of the Jar Test to the full-scale treatment plant can be a complex process. The conditions in the lab, such as the mixing and settling conditions, may not perfectly replicate the conditions in the plant. Therefore, it is important to adjust the treatment conditions as necessary based on the performance of the plant.
It is also important to consider the cost and availability of the coagulant and flocculant chemicals. While the Jar Test may indicate that a certain chemical is the most effective, it may not be the most cost-effective or readily available option. Therefore, it is important to consider all factors when deciding on the best treatment option.
Environmental Impact of Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and flocculants are necessary for effective wastewater treatment, but they can have negative environmental impacts. These chemicals can be toxic to aquatic life, and can also contribute to the formation of harmful byproducts. Therefore, it is important to use these chemicals judiciously, and to explore other treatment options where possible.
There are also environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional coagulants and flocculants, such as natural polymers and inorganic polymers. These alternatives can be more expensive and may not be as effective for certain types of wastewater, but they can be a good option for reducing the environmental impact of the treatment process.
Conclusion
The Jar Test is a valuable tool for optimizing the wastewater treatment process. It allows for the simultaneous comparison of different treatment options, providing valuable insights into the most effective treatment method. However, it is important to be aware of its limitations, and to adjust the treatment conditions as necessary based on the performance of the full-scale plant.
It is also important to consider the cost and environmental impact of the coagulant and flocculant chemicals. While these chemicals are necessary for effective treatment, they can be expensive and may have negative environmental impacts. Therefore, it is important to use these chemicals judiciously, and to explore other treatment options where possible.



