
Demystifying the Mechanics of LAN Networks
Local Area Networks (LANs) are the backbone of many business operations, providing a secure and efficient method of communication and data transfer. But how do these networks function? Let's delve into the intricate world of LAN networks and unravel their workings.
The Basics of LAN Networks
LAN, or Local Area Network, is a network of computers and other devices that share a common communications line or wireless link within a small geographical area. This could be within a home, office, or a group of buildings. The primary purpose of a LAN is to allow for the sharing of resources and information.
LANs are characterized by their high data transfer rates and relatively small geographical coverage. They are typically owned, controlled, and managed by a single person or organization, providing a high level of control over network security and performance.
Components of a LAN Network
A LAN network comprises several key components. First, there are the computers, also known as nodes, which are the devices connected to the network. These could be desktop computers, laptops, or even mobile devices.
Second, there are the networking devices, which include switches, routers, and hubs. These devices help to manage the data traffic on the network, ensuring that data packets are sent and received correctly.
Lastly, there are the cables or wireless technologies that connect the devices. These can range from Ethernet cables to Wi-Fi connections, depending on the specific requirements of the LAN.
How LAN Networks Function
LAN networks operate by connecting devices using a network protocol, which is a set of rules for data communication. The most common protocol used in LANs is the Ethernet protocol, although others like Token Ring or Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) can also be used.
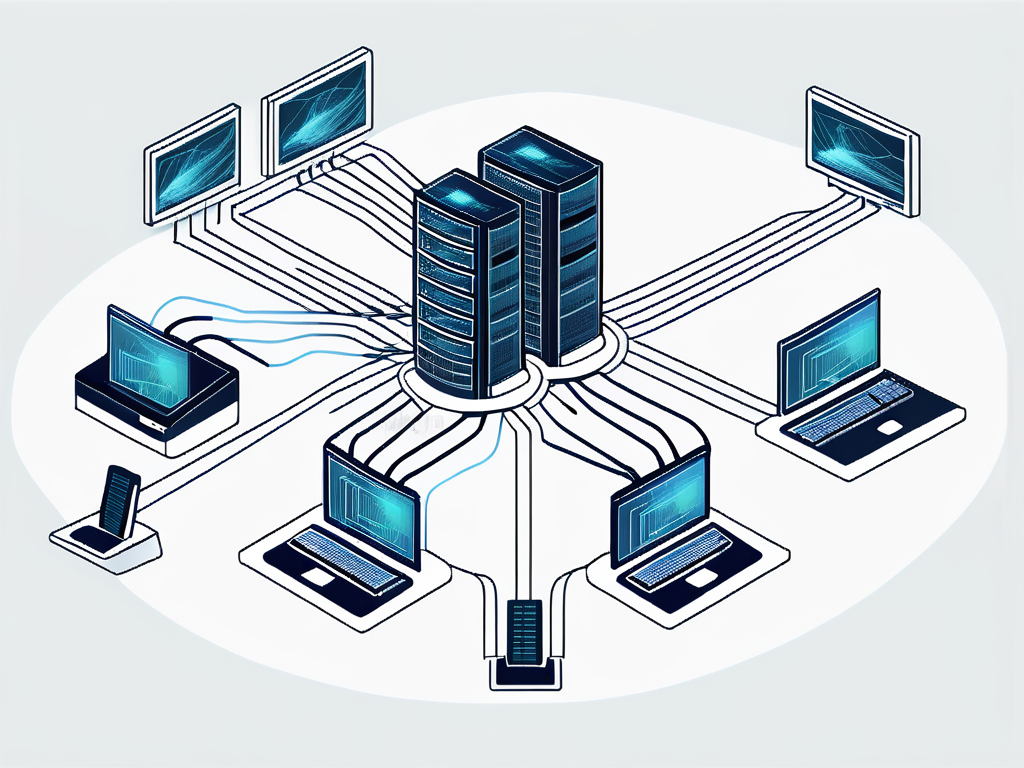
When a device wants to communicate with another device on the network, it sends a data packet addressed to that device. Networking devices, like switches or routers, read the address and direct the packet to the correct destination.
Data Transmission in LAN Networks
Data transmission in a LAN network occurs in the form of packets. A packet is a small amount of data sent over a network. Each packet contains the source address, the destination address, and the data itself.
When a packet is sent from one device to another, it is first broken down into smaller pieces, or frames. These frames are then sent individually over the network and reassembled at the destination device.
This method of data transmission allows for efficient use of network resources, as multiple devices can send and receive data simultaneously without causing a traffic jam on the network.
The Role of LAN Networks in Today's World
LAN networks play a crucial role in both personal and professional settings. In the business world, LANs enable employees to share resources and collaborate effectively, regardless of their physical location. They also provide a secure environment for sensitive data, as the network's owner has complete control over its security settings.
In the home setting, LANs allow for the sharing of internet access, printers, and other resources among multiple devices. They also enable multiplayer gaming, media streaming, and other forms of entertainment.
The Future of LAN Networks
As technology continues to evolve, so too will LAN networks. We can expect to see advancements in wireless LAN technologies, providing faster and more reliable connections. Additionally, as more devices become network-capable, we will likely see an increase in the size and complexity of LAN networks.
Despite these changes, the fundamental principles of how LAN networks work will remain the same. Understanding these principles is the key to effectively managing and troubleshooting a LAN network.
Conclusion
Understanding how LAN networks work is not just for IT professionals. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, having a basic understanding of these networks can be beneficial for anyone. Whether you're setting up a home network or managing a business network, the principles of LAN networks remain the same.

By understanding how these networks function, you can ensure that your network is set up correctly, troubleshoot any issues that arise, and make informed decisions about your network's future. So the next time you connect to a LAN network, remember the intricate processes that make it all possible.
